“He who controls trades controls freedoms”
Satoshi Nakamoto
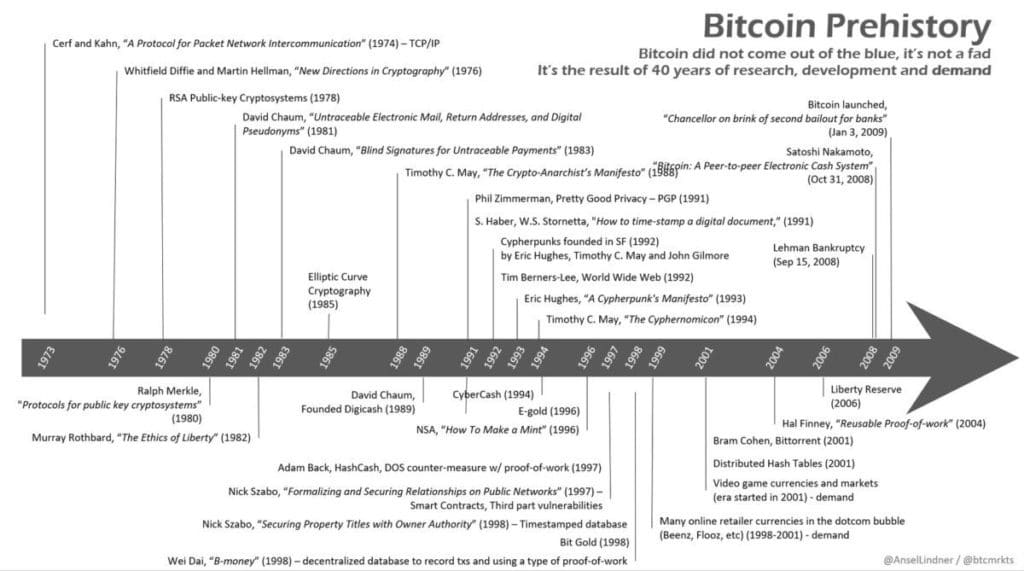
On October 31, 2008, the Bitcoin whitepaper, “Bitcoin, Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”, was published by a certain Satoshi Nakamoto. This anonymous person unveils to the public his technological innovation, Bitcoin (BTC), its stakes, and the philosophy behind its creation. After all these years his identity is still a mystery and probably destined to remain so. The creator of BTC advocated digital decentralization, considering that the advent of the Internet could bring new problems, particularly with regard to privacy and the centralization of technological power.
There is no doubt that Satoshi Nakamoto and the Cypherpunks were strongly inspired by the fears exposed by George Orwell in his book “1984”. His original work has marked generations and popular culture. In this famous dystopian novel, the author describes Great Britain as controlled by totalitarianism. “Big Brother” controls the lives and thoughts of individuals in the smallest details of their lives and freedoms are prohibited.
This fear has probably motivated crypto-anarchists and Cypherpunks to fight against the abuses of digital technologies, at least one of whose members would have possibly participated in the creation of Bitcoin or would even be THE creator.

On January 3, 2009, the first block of Bitcoin was mined by Satoshi Nakamoto himself, while the first BTC was transferred to Hal Finney, a prominent Bitcoin figure and cryptocurrency pioneer. Satoshi Nakamoto’s anonymity is more important than just privacy, it is proof of the decentralizing nature of blockchain technology and Bitcoin.
If the speculations on the identity of Satoshi Nakamoto are going on, this mystification of its character, of his story offers to this technology and its popularity a global and mystical scope, arousing the curiosity of the most curious or the assurance of a pure and effective decentralization of his technology for the most skeptical.
The origin of Bitcoin
Bitcoin and its technology, the Blockchain, are the result of decades of thinking and innovation in digital technology. The desire of cryptographic experts was to safeguard the user’s personal privacy from the Internet.
If the Internet is a tool of decentralization, a bad design of protocols would allow centralized powers to reverse this trend into a totalitarian policy. While George Orwell described a dystopian world in which “futuristic” technologies would tend to enslave individuals, we can see that GAFAM are overstepping their function and interfering in private lives for economic purposes.
If the centralized entities [GAFAM] have set out the paths that have allowed the construction of the Internet revolution, it is nevertheless noticeable that the States and the Digital Giants have seized this power and have subjected the users of this network to their economic strategy and their vision of the world.
This period of centralization, if it can be criticized, was eventually necessary in order to produce wealth and innovations. Satoshi Nakamoto and the Cypherpunks were already denouncing, in the 1990s, this centralization that is harmful to the Internet. The manifesto of a cypherpunk published in 1993 by Eric Hughes exposed this thought.
Cryptography facing the “problems of the Byzantine generals
The “Byzantine Generals” Problem is a computer science concept. This metaphor exposes a problem of trust in the communication of information: As the army of the Byzantine Empire plans to lay siege to a city, the army’s generals can only communicate through oral messengers in order to coordinate a strategy, offensive or defensive. But some of them are traitors and try to distort the information. The issue is to find a strategy to ensure that all the loyal generals can reach a consensus. This problem is mainly encountered in peer-to-peer networks.
Bitcoin, for example, is based on a proof-of-work consensus protocol on the blockchain. This type of algorithm is called, “Byzantine Fault Tolerance“, abbreviated as BFT. The remuneration of the validators / miners increases the interest in running the network rather than attacking it.
Nakamoto’s innovation was to allow numerous nodes to participate in a completely open manner without hindering the proper functioning of the protocol. Thus, the security of the network with respect to its “treacherous” validators is greatly increased.
The “spiritual father” of Cypherpunks
In the early 1980s, Dr. David Chaum, a cryptographer, published the first articles that introduced the “original” topic of cryptocurrencies and reputation-based economies: “Security Without Identification: Transaction Systems to Relegate Big Brother to the Museum.”
In 1983, this man created the first digital currency, ecash. A St. Louis bank named “Mark Twain Bank”, decided to test its viability in micropayments. But the acquisition of this bank by the Mercantile Bank put an end to the project. The main mistake of the project was to centralize its management, which implied dependence on banks.
The first stones of the cryptographic and digital revolution are laid, but many problems are still to be solved. How to no longer depend on institutions and at the same time not to be subjected to an equally powerful force such as an actor who would control the monetary supply?
The Cypherpunks
We, the Cypherpunks are dedicated to building anonymous systems. We are defending our privacy with cryptography, with anonymous mail forwarding systems, with digital signatures, and with electronic money.
Eric Hughes, The Cypherpunk Manifesto
In the 1990’s, cryptographers first met in San Francisco to develop David Chaum’s ideas, until they created an e-mail list that they named “Cypherpunk“. In 1992, Tim May published the “Crypto-anarchist Manifesto”, which states his anarcho-capitalist orientation in order to demonstrate that computer science is a way of development for capitalist anarchism.
According to the author, the crypto-anarchy would allow, thanks to cryptological processes, to bypass the governmental authorities and the big companies in the economic transactions. The network encryption allows anonymizing the discussions or the transactions and to eliminate the intermediaries, illegitimate according to the anarchist philosophy. Cypherpunks are part of this ideological movement, the impulse of freedom of the Internet has launched a new era of possibilities.
- Jacob Appelbaum: The original developer of TOR.
- Julian Assange: founder of WikiLeaks.
- Dr Adam Back: inventor of hashcash, co-founder of Blockstream.
- Bram Cohen: creator of BitTorrent.
- Hal Finney: lead author of PGP 2.0, the original creator of the reusable Proof-of-Work.
- Philip Zimmermann: creator of PGP 1.0
The Cypherpunk Manifesto
“No one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence, nor to attacks upon his honor and reputation. Everyone has the right to the protection of the law against such interference or attacks.”
Art. 12, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, 1948
The Cypherpunk Manifesto is a plea for privacy, published on March 9, 1993, on the site activism.com, it defends the idea that digital technologies could undermine many fundamental principles. In the words of Eric Hughes, privacy and anonymity which are core principles of our society would be misguided by the digital. “An anonymous exchange system would reinforce the power of the individual to reveal their identities when they wish and only when they wish, which is the essence of privacy”.

He believes that digital privacy indispensably requires cryptography, so that everything is heard only by those for whom the message was intended, if the message is openly available to the world, then there is no personal privacy. “To encrypt is to indicate a desire for privacy, and to encrypt with weak cryptography is to indicate a weak desire for privacy”. However, we notice today that digital companies have monetized our private life, the Cypherpunk’s observation was right and exactly meets the needs of the new “digital individuals”.
Their goal was to build privacy-friendly software, so they released their own open-source code to allow personal privacy advocates to build this ecosystem. The will to change things, to trust individuals and their discernment, is probably what allowed them to build such a cryptographic system. Their desire was to implement a social contract in which “the individuals” will be the only actors and pillars, by defending their fundamental interests such as privacy.
Satoshi Nakamoto creates Bitcoin
On October 31, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto revealed the Bitcoin Whitepaper, detailing the functioning of his digital currency and revealing the stakes involved in its creation. In a desire to decentralize exchanges between individuals, he developed a complex protocol allowing the exchange of a digital currency without intermediaries thanks to the blockchain and smart contracts. A few days after the publication of the white paper, he registered the project on an open source code platform called SourceForge
On January 3, 2009, as the subprime crisis rocked the world, Satoshi Nakamoto put his innovation into action; he mined the first block of BTC. While Cypherpunks themselves believed that too many obstacles would hinder the development of a digital currency, Satoshi Nakamoto’s solution was the complete decentralization of the cryptocurrency. With the blockchain, he was not only introducing a revolutionary technology, but also a revolutionary political concept. The total and effective decentralization of the network was essential for the proper functioning of a cryptocurrency protocol as we see it today.

Inside the Genesis block, Satoshi left a message that read “The Times newspaper 03/Jan/2009: UK chancellor is about to bail out banks for the second time”. Many people interpreted it as an assessment of the current monetary system, while others saw it as a time stamp for Nakamoto. This message has also been the subject of theories as to the identity or location of Satoshi Nakamoto, assuming that he was from London.
But who Satoshi Nakamoto really is ?

This emblematic and mystical figure of the crypto ecosystem and the Web3 revolution has been the subject of many investigations and theories as to his identity. It is worth mentioning that. Dan Kaminsky, a computer security researcher, claimed that Satoshi Nakamoto is a genius in many ways or most certainly he was a group of individuals.
The following names were found in the creators’ identity investigations:
- Nick Szabo.
- Dorian Nakamoto.
- Hal Finney.
- Craig Steven Wright.
- Adam Back
- “A Londoner”
His anonymity, the mystery that surrounds him, is part of the project, it is even the keystone of it. If the members of Cypherpunk were obviously the first to be suspected of hiding behind the identity of this 21st century genius, it is likely that this is the case. It is likely that this is the case, but it is essential not to know and let the mystery continue. Now, his personal net worth is estimated at more than 60 billion dollars, making him the 20th richest person on the planet.
Conclusion
“An anonymous system reinforces the power of individuals to reveal their identities when they want to and only when they want to; this is the essence of privacy.”
Eric Hughes in the 1993 “Manifesto of a Cypherpunk”.
Satoshi Nakamoto’s project to decentralize trades and interactions through the internet has launched a real technological revolution. Bitcoin is now publicly known, it is now the center of attention of state and banking institutions. It is attracting the interest of both individuals and institutional funds, and the anonymity of its creator has played a major role in the development of Bitcoin.
This cryptocurrency belongs to no one and therefore to everyone, the Proof-of-Work consensus protocol allows each individual to become an actor in this network. It is therefore no longer the role of a central bank to “control the currency” but for individuals to decide its future. Bitcoin could have been a failure like its fallen namesakes, but the will of individuals has always and will continue to enable these major transformations of society.
What if basing your currency on people’s trust was the best solution? It is very likely that Satoshi Nakamoto is a single person, heir to the philosophy and thoughts of Cypherpunks. In order to hold such a huge secret that is fundamental to his technology, only one person would theoretically be able to keep the secret, if not a very small group of people with remarkable trust and determination.
Sources
- https://satoshi.nakamotoinstitute.org/
- https://www.cnews.fr/monde/2021-02-03/linventeur-du-bitcoin-satoshi-nakamoto-est-lune-des-personnes-les-plus-riches-du
- https://www.actualitefinanciere.fr/crypto-monnaies/7-points-pour-savoir-qui-est-satoshi-nakamoto-00012851.html
- https://www.mtimicrofuelcells.com/des-articles/programmes-du-gouvernement-americain-axes-sur/
- https://www.businessinsider.fr/qui-se-cache-derriere-satoshi-nakamoto-le-mysterieux-createur-du-bitcoin-aux-nombreuses-identites-presumees-186739
- https://www.labourseauquotidien.fr/bitcoin-lecon-cypherpunks/
- https://www.activism.net/cypherpunk/manifesto.html




